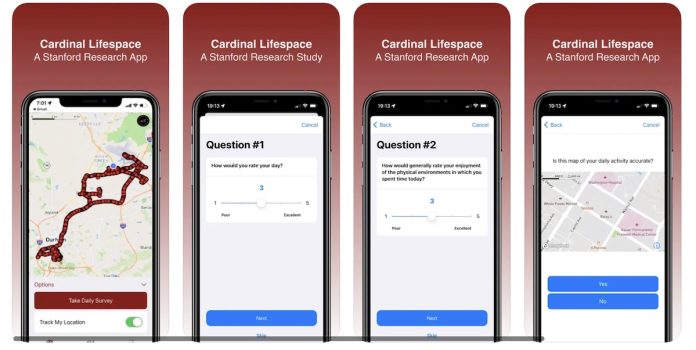
Stanford University researchers launched a research study that helps develop individual life space maps.
The central idea behind the research study is to evaluate how environmental conditions influence health.
To that end, the researchers have developed a novel measure of the space within which individuals live and move.
The LifeSpace app, built with the CardinalKit framework, creates individual life-space maps using Global Positioning System (GPS)-based methods.
Related Reading:
- Apple Health is not TikTok and other conversations with Dr. Oliver Aalami (post-WWDC Insight Series)
- Stanford Biodesign-based Zeit Medical to leverage EEG wearable and sophisticated AI to detect early stroke event
- Stanford develops a new wearable sensor to detect stress hormones
Studying where people spend most of their time
According to the researchers, there is ample data on the influence of the environment on health, but most studies have examined residential addresses as the primary environment.
“Our study will advance this research by including data on where people spend their time. By mapping the space within which individuals live and move, we can study features of the social and built environment that support health, and identify opportunities for intervention to protect disadvantaged communities.”
LifeSpace is conducted in partnership with the REGARDS study (Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke ), sponsored by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which has followed participants for over a decade to understand why Southerners and Black Americans have higher rates of stroke and related diseases that affect brain health.
To participate in the Study, you must create an account through the LifeSpace App. You must affirmatively consent to participate in the study before creating your account.
Your data will be used for research only. LifeSpace Researchers will NOT use your data for commercial advertising.
The team spearheading the new research study includes Michelle Odden, Ph.D., Annabel Tan MPH, and Vishnu Ravi, MD.
You can read more about this exciting research study on the Cardinal LifeSpace website.